Here’s a breakdown of dog cavities (dental caries), with key takeaways for dog owners:
What Are Dog Cavities?
- While less common than in humans, dogs CAN get cavities.
- It’s a destructive process where bacteria eat away tooth structure, causing holes.
- If the cavity reaches the tooth’s nerve (the pulp), it causes pain and infection.
Causes of Cavities
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Plaque buildup is the main culprit, making teeth vulnerable.
- Sugary/Starchy Foods: Just like for us, these fuel cavity-causing bacteria.
- Genetics: Some breeds are more prone to dental issues.
- Damage to Teeth: Chips and cracks provide entry points for bacteria.
Symptoms: Warning Signs
- Bad breath (beyond normal doggy breath)
- Dark spots or holes on teeth
- Painful chewing, avoiding hard foods
- Reluctant to have mouth touched
Why Early Treatment Matters
- Cavities HURT. Don’t let your dog suffer silently.
- Infection can spread from the tooth, causing serious health problems.
- In severe cases, tooth loss is possible.
Treatment
Sadly, dog cavities aren’t fixed with simple fillings like ours. Treatment depends on how bad things are:
- Early Stage: Special solutions might help if damage is minor.
- Advanced Cavities: Often require tooth extraction under anesthesia.
Prevention is KEY
- Regular Brushing: Special dog toothbrushes and pastes are a MUST.
- Dental Chews: These help scrape off plaque (but don’t replace brushing).
- Vet Checkups: Catch problems early, and get professional cleanings.
- Balanced Diet: Avoid sugary treats, and ask your vet about food choices.
Key Takeaways
- Don’t think “dogs don’t get cavities”. They DO, though less often than us.
- Bad breath is often the FIRST sign – don’t ignore it!
- Work WITH your vet to create a dental care routine for your dog.
- Think of it as protecting your dog’s smile and overall health!
What Are Cavities in Dogs?
Caries in dogs are recorded quite rarely; the frequency of occurrence of this pathology in veterinary practice is about 0.5% of the total number of oral diseases.
This is explained by the fact that dog saliva is highly alkaline, which prevents the formation of an acidic environment and subsequent demineralization of the enamel. Therefore, only when the pH of saliva shifts to the acidic side, favorable for pathogenic microorganisms, can a carious cavity occur.
Often, during an appointment, it is not possible to conduct a detailed examination of the outermost teeth on the upper and lower jaws of the molars. These teeth, as a rule, are most often exposed to carious lesions in dogs due to the existing small interdental spaces and occlusal interaction with the antagonist’s teeth.
Usually, the lesion affects fissures (anatomical depressions) on the chewing and lateral surfaces of the teeth in places that are difficult to access. Therefore, caries is most often detected during dental procedures under anesthesia. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that animals may not demonstrate toothache at all, but only show it in later stages, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis in the early stages.
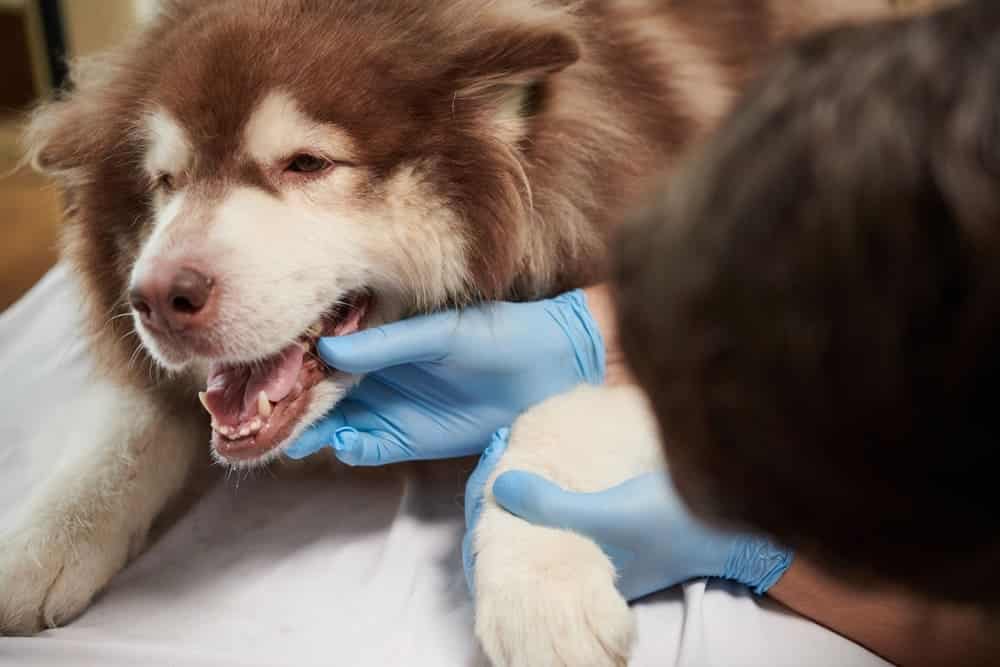
To conduct a full diagnosis, it is important to conduct a visual assessment, instrumental probing, and a dental X-ray examination of the affected tooth, on the basis of which a final diagnosis can be made and the degree of damage to a particular tooth can be judged, determining the necessary treatment tactics.
By analyzing the results of dental x-rays of the affected tooth, it is possible to identify oval enlightenments in the crown area, indicating loss of tooth structure (enamel and dentin). There are also signs of periapical inflammation in the area of the distal root due to the opening of the pulp chamber and infection.
In view of the identified pathology, it was decided to remove the distal root involved in the inflammatory process and preserve the 2 remaining roots through pulp extraction, filling, and fixation of a light-curing filling.
Thus, based on the x-ray diagnostic method, it is possible to confirm the diagnosis of “deep dental caries in dogs”, as a result of which the pulp chamber was exposed, which resulted in the occurrence of a complicated form of caries.
Causes Of Cavities in Dogs:
Tooth decay in dogs can occur for a variety of reasons and is often the result of several factors. One of the main reasons is insufficient care of the dog’s oral cavity and teeth. Poor diet, lack of regular tooth brushing, and failure to see a veterinarian for preventative checkups can lead to plaque and tartar buildup, which contributes to the development of tooth decay.
Another factor contributing to the occurrence of caries in dogs is an imbalance of microflora in the oral cavity. The presence of certain bacteria can lead to the destruction of tooth enamel and the formation of cavities. Also influencing the development of caries are genetic factors that can make a dog’s teeth more susceptible to decay.
Tooth decay in dogs can also be caused by long-term use of certain medications that have a negative effect on the condition of the teeth. Not having enough minerals and vitamins in your dog’s diet can also contribute to the development of tooth decay. In addition, tooth decay can be caused by tooth trauma or damage to the enamel as a result of improper use of hard objects when chewing.
In addition to cavities, other health concerns like maggots can also arise due to poor care. Understand the signs and preventive measures for such conditions.” can refer to How to Tell if Your Dog Has Maggots.
Poor Quality Dog Food:
Poor nutrition is one of the main causes of tooth decay in dogs. Unfortunately, many owners do not pay enough attention to the quality of food they provide to their pets. The dog’s diet should be balanced and contain all the necessary nutrients.
One of the main problems of poor nutrition is excessive consumption of sweet and starchy foods. Dogs should not consume sugar and sweets, as this promotes the growth of bacteria in the mouth and the development of tooth decay. Also, excess consumption of starch can lead to the formation of plaque and caries.
It is also important to consider that feeding your dog table scraps can lead to dental problems. Some foods that people consume without harm to their health can be dangerous for a dog’s teeth. For example, poultry or fish bones can lead to fractures and damage to teeth. Also, some products may contain ingredients that cause tooth decay.
To prevent caries in a dog, it is necessary to provide it with proper and balanced nutrition. The diet should include fresh and high-quality food, and also take into account the individual characteristics of the pet. Regular dental cleanings and checkups with your veterinarian will also help prevent tooth decay.
Insufficient Oral Care:
Insufficient oral care is one of the main causes of tooth decay in dogs. Just like in humans, regular tooth brushing and oral care are important to maintaining healthy teeth and gums in dogs.
Lack of regular brushing and some bad habits can lead to the formation of plaque and tartar. Plaque is a soft, white film of bacteria and food debris that accumulates on and between teeth. If plaque is not removed regularly, it can harden and turn into tartar, which can lead to gum inflammation and tooth decay.
Some bad habits, such as feeding your dog soft and sticky foods, or excessive consumption of sweet or sour foods, can also contribute to the development of tooth decay. These products can remain on the teeth and gums, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to grow and cause tooth decay.
To prevent tooth decay in dogs, it is necessary to regularly brush their teeth using special toothbrushes and toothpaste for animals. It is also recommended to have your teeth professionally cleaned by a veterinarian periodically. It is important to remember that poor oral care can lead not only to tooth decay but also to other serious problems such as gum disease and tooth loss.
“Proper breathing is also crucial for your dog’s overall health. Learn how to ensure your canine friend is breathing well, which is just as important as dental health.” can refer to How to Help a Dog Breathe Better
Symptoms Of Cavities In Dogs:
Tooth decay in dogs is a serious condition that can lead to pain, infection, and tooth loss for your pet. Early detection and treatment of tooth decay is very important to keep your dog’s teeth healthy. If you suspect your dog has tooth decay, look for the following symptoms:
Increased Tooth Sensitivity:
Increased tooth sensitivity in dogs can be a sign of advanced tooth decay. Caries is a chronic dental disease that destroys tooth enamel and dentin. As a result of this, the nerve endings of the teeth become more sensitive to irritants.
If your dog has sensitive teeth, he or she may experience pain or discomfort when eating or chewing. She may avoid hard or cold foods and may be afraid to touch her teeth. This symptom is often accompanied by changes in the dog’s behavior, such as irritability or disobedience.
Treatment of dental hypersensitivity is associated with eliminating the causes of caries and restoring the affected teeth. The dentist must conduct an examination and identify all tumors, cracks, and cavities in the tooth or teeth. After this, depending on the condition of the teeth, a decision can be made on a treatment protocol, including conservative treatment, tooth extraction, or complete restoration.
Formation of Dark Spots on Tooth Enamel:
The formation of dark spots on tooth enamel can be a sign of tooth decay in dogs. The appearance of these spots can be caused by various factors, such as poor oral hygiene, poor diet, genetic predisposition, or exposure to harmful substances.
One of the main reasons for the formation of dark spots on the tooth enamel in dogs is poor oral hygiene. Poor or insufficient brushing of teeth leads to the accumulation of plaque, which promotes the growth of bacteria and the formation of cavities. As a result, dark stains may appear on the teeth, which can even penetrate deep into the enamel.
Another reason for the formation of dark spots on tooth enamel may be poor nutrition. When eating foods containing large amounts of sugar or acids, tooth enamel can be destroyed. As a result, dark spots may appear on the teeth, which may be a sign of the early stages of caries.
Genetic predisposition can also cause dark spots to form on the tooth enamel in dogs. If one or both parents had dental problems, there is a good chance that the offspring may also have problems with tooth enamel. In this case, dark spots on the teeth may be a sign of a hereditary predisposition to caries.
Bad Breath:
Bad breath is one of the most common symptoms of tooth decay in dogs. It can be caused by various reasons and indicates problems with the oral cavity or digestive system.
One of the main causes of bad breath in dogs is the presence of tartar. The accumulation of plaque and bacteria on teeth leads to the formation of a hard deposit called tartar. As a result of this process, bacteria continue to multiply and produce toxins, resulting in an unpleasant odor.
Another cause of bad breath in dogs can be gum disease such as gingivitis and periodontitis. These diseases are characterized by gum inflammation and tissue destruction, which can also cause an unpleasant odor.
Additionally, bad breath can be caused by problems with the digestive system. Some diseases of the stomach and intestines can cause an odor that can spread through the mouth.
To eliminate bad breath in dogs, you need to consult a veterinarian. The doctor will examine the oral cavity and give recommendations for further treatment. Depending on the cause of the odor, tartar removal, gum disease or digestive system treatment may be required.
Treatment Of Cavities in Dogs:
Treatment of caries in dogs is complex. Includes both medical and surgical treatment. The superficial stage of caries development allows the affected area to be treated with a special substance – silver nitrate in combination with sodium fluoride. Advanced stages require surgical removal of the affected one or more teeth.
The animal is given local anesthesia or put under deep anesthesia. The latter is preferable since the doctor can carry out the manipulation without much difficulty. A tooth with caries that is not removed in a timely manner can cause serious complications. An infection in a tooth spreads to the entire jaw.
Over time, the possibility of blood infection and the development of inflammatory processes in the membranes of the brain, ending in the death of the pet, cannot be ruled out.
You can prevent the development of caries in your dog by following the rules of prevention. From a very early age, the owner of the dog must teach the puppy to carry out hygiene procedures.
It is necessary to monitor your pet’s health by brushing your teeth to remove plaque. High-quality cleaning is carried out several times a week. For these purposes, it is important to purchase a special brush and paste.
A special place in the prevention of caries is occupied by the preparation of a diet. The pet’s menu should be varied, food is selected depending on the individual needs of the animal. High-quality feed does not require the introduction of additional mineral and vitamin supplements into the diet, which cannot be said about natural feeding. It is recommended to consult a veterinarian first.
How To Prevent Cavities in Dogs:
Specific signs of the development of a carious tooth are changes in the shade and density of the tooth structure. The dog loses its appetite, refuses solid food, and a repulsive putrid smell comes from its mouth.
The first signs of a pathological process are a reason to immediately contact a veterinary clinic for help. During the examination, the doctor will assess the degree of neglect of the situation and prescribe adequate therapy, which will prevent serious complications.
To prevent caries in dogs, you need to:
- Maintain your pet’s oral hygiene at home by using a specially selected brush/veterinary paste and alternating between brushing teeth and applying gels to prevent plaque formation;
- Carry out professional ultrasonic cleaning in a clinic with a veterinary dentist;
provide balanced feeding; - Monitor the amount of carbohydrates your dog consumes in his diet;
- Do not allow chewing on super-hard objects (sticks, bones, and deer antlers), but use a special line of dental treats and toys;
- Attend preventative visits to evaluate your oral health.
“Alongside maintaining dental health, regular grooming and cleaning are essential for your dog’s well-being. Discover the best ways to keep your dog clean and healthy.” can refer to How to Clean a Dog.
Conclusion:
The appearance of characteristic signs is a reason to immediately contact a veterinary clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe a number of necessary tests. Diagnosis of caries is not difficult.
Laboratory tests are prescribed, and a blood test is especially important. The results obtained make it possible to assess the degree of neglect of the pathology – the presence of inflammation in the body. Sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out during an examination at a veterinary hospital, and in case of urgent need, the affected tooth of the dog is removed.