Here’s a comprehensive guide about sebaceous adenoma in dogs, covering causes, diagnosis, treatment and key takeaways:
Understanding Sebaceous Adenoma in Dogs
- What is it? A sebaceous adenoma is a benign tumor arising from the sebaceous glands, which produce oil (sebum) that lubricates your dog’s skin and hair. These tumors are typically harmless but can become problematic if they rupture or become infected.
- Common in Older Dogs: Sebaceous adenomas primarily affect older dogs as their bodies undergo age-related changes.
- Breed Predispositions: Some breeds, like Poodles, Cocker Spaniels, and Basset Hounds, are more susceptible to developing this condition.
Causes
- Unknown Exact Cause: The precise reason for sebaceous adenomas is not fully understood, but factors contributing to their development include:
- Age-related changes
- Genetics in certain breeds
- Previous inflammation or injuries around sebaceous glands
Symptoms
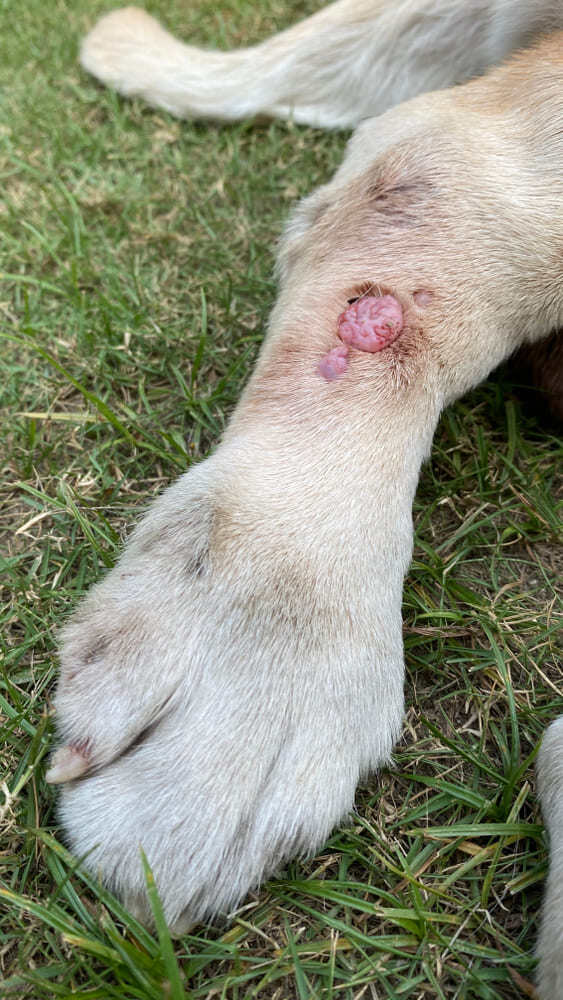
- Lumps Under the Skin: The most obvious sign is the appearance of round, movable lumps under your dog’s skin. These can vary in size.
- Ulceration: In some cases, the tumor may break open, creating an ulcer.
- Itching and Licking: Your dog may lick or scratch at the area.
- Infection: If the lump becomes infected, you might notice redness, swelling, or discharge.
Diagnosis
- Veterinary Exam: Your vet will carefully examine your dog’s skin and possibly take a sample of the lump for further testing.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken to examine the cells under a microscope, confirming the type of tumor.
- Additional Tests: X-rays or ultrasound may be used to assess the extent of the tumor and its impact on surrounding tissues.
Treatment
- Monitoring: If the tumor is small and causing no problems, your vet may recommend simply observing it for changes.
- Surgical Removal: For larger tumors or those causing discomfort, surgical removal is the most common treatment. This ensures complete excision and reduces the risk of recurrence.
- Additional Treatment: In rare cases of malignancy, further therapy like chemotherapy or radiation might be necessary.
Prevention
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent sebaceous adenoma, these measures can help:
- Regular Grooming: Bathing and brushing your dog helps maintain healthy skin and sebaceous gland function.
- Balanced Diet: Provide a high-quality diet for overall health and skin support.
- Exercise: Regular exercise promotes good circulation and immune system function.
- Vet Checkups: Routine exams help detect any skin changes early on.
Key Takeaways
- Sebaceous adenomas are generally benign but still require veterinary attention.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.
- Older dogs and certain breeds are more prone to this condition.
- Simple preventive measures can contribute to your dog’s overall skin health.
Important Note: If you notice any lumps or bumps on your dog’s skin, don’t hesitate to consult your veterinarian. While most are harmless, it’s always better to have them professionally assessed for peace of mind and to ensure your furry friend gets prompt treatment if needed.
What Is a Sebaceous Adenoma Dog?
A sebaceous adenoma is a tumor that forms from the sebaceous glands located under the skin of a dog. The reason for its appearance is hyperplasia, that is, excessive growth of glandular tissue. The most common form of sebaceous gland adenoma in dogs is the sebaceous adenoma.
Sebaceous gland tumors can form on any part of a dog’s body, but they most often occur on the head, neck, back, and tail. Sebaceous gland adenomas can be single or multiple and have different sizes.
The sebaceous cyst in dogs is a small growth, often benign and painless. Despite everything, any cyst in dogs deserves to be taken seriously: its presence can be a sign of a more serious health problem, such as a tumor.
The sebaceous cyst is caused by the accumulation of sebum under the dog’s skin. It is usually triggered by too much activity of the sebaceous glands. Sebum is a fairly fatty substance that protects the dog’s skin.
This overproduction of this substance forms a tiny ball under the dog’s skin when a sebaceous cyst occurs. For the dog, the sebaceous cyst poses little threat or harm. If the wound is left untreated, it may puncture itself and result in a bacterial infection.
Causes Of Sebaceous Adenoma In Dogs:
Sebaceous gland adenoma may be preceded by various inflammatory processes in the gland area. They can occur as a result of infections, injuries, or even simply due to clogged sebaceous gland ducts. Constant irritation and inflammation can provoke tissue hyperplasia and adenoma formation.
Some dog breeds also have an increased predisposition to developing sebaceous gland adenomas. For example, poodles, cocker spaniels, and basset hounds are at greater risk of developing this disease.
Moreover, age may also play a role in the occurrence of adenoma. Aging dogs are at increased risk of developing sebaceous gland tumors.
It is important to note that the exact causes of sebaceous gland adenoma in dogs are not fully understood. A combination of different factors and their interaction can lead to the emergence and development of this pathology.
How To Recognize Sebaceous Adenoma in Dogs?
The appearance of a lump on the dog’s skin deserves to be taken seriously. Because if sebaceous cysts are benign, certain cysts can indicate the presence of a more or less significant tumor.
Several signs can tell you that your dog is suffering from a sebaceous cyst:
- The cyst looks like a small ball of skin that may be slightly white;
- The size of the sebaceous cyst does not change over time;
- If the sebaceous cyst pierces, a greasy and sticky substance spreads.
Conversely, if the cyst seems painful for the dog or if it grows quickly, it is not a sebaceous cyst. In any case, it is better to consult a veterinarian if you notice a cyst in your dog.
Symptoms of Sebaceous Gland Adenoma in a Dog:
Symptoms of sebaceous gland adenoma in dogs include the appearance of round, movable tumors under the skin that can vary in size; perhaps spontaneous contraction or spontaneous breakthrough of the tumor; the appearance of pain, bleeding, infection, and inflammation in the tumor area; deterioration of the dog’s general condition – apathy, fatigue, loss of appetite.
The main symptoms of sebaceous gland adenoma in a dog:
- Formation of round or oval tumors Sebaceous gland adenoma in a dog manifests itself in the form of one or more dense and mobile tumors, which can be of different sizes and localized on the neck, back, abdominal cavity, and other parts of the body.
- Possible formation of ulcers on the surface of the tumor In some cases, a sebaceous gland adenoma in a dog can cause the development of ulcers on the surface of the tumor, which can lead to infection and additional complications.
- Itching and licking of the tumor Dogs with sebaceous adenoma may experience itching and constantly lick the surface of the tumor.
- Peeling and redness of the skin Some dogs with sebaceous gland adenoma may have peeling and redness of the skin around the tumor.
- Foci of inflammation or infection Sebaceous gland adenoma can be complicated by inflammation or infection, which is often accompanied by an increase in tumor size and pain.
Diagnosis Of Sebaceous Gland Adenoma in a Dog:
At the initial visit, the veterinarian conducts a thorough physical examination of the dog, assessing the general condition of the animal and checking for diseased glands.
With a sebaceous gland adenoma, the following symptoms may be noticed: an increase in the size of the gland, tumor formation, redness, and possibly the formation of an ulcer on the surface.
For an additional and more accurate diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe procedures such as a biopsy, cytological analysis, or histopathological examination. During a biopsy, the doctor takes a tissue sample from the affected gland and sends it for laboratory testing to determine the presence of malignant cells.
The cytological analysis allows you to determine the nature of the cells in the sample. In the case of sebaceous adenoma, atypical cells may be found, which may indicate the presence of a tumor. Histopathological examination is a detailed examination of tissue under a microscope to determine the structure of the tumor and its nature.
In addition, the doctor may order additional instrumental tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, to assess the extent of the tumor and the possible impact on surrounding tissues and organs.
All of these methods help the doctor determine the diagnosis and develop a treatment plan for a dog with sebaceous gland adenoma. Early diagnosis and the possibility of surgery play an important role in predicting the outcome of treatment and the well-being of the animal.
Prevention Of Sebaceous Gland Adenoma in Dogs:
Prevention of sebaceous gland adenoma in a dog includes a number of measures aimed at maintaining health and preventing the occurrence of this disease.
First of all, it is necessary to monitor the dog’s hygiene. Regular washing and cleaning of the coat with special products will help prevent the accumulation of sebaceous glands and the formation of adenomas.
It is also important to pay attention to your diet. A properly balanced diet consisting of high-quality dry or natural food will provide the dog with the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Regular exercise also helps prevent sebaceous gland adenoma in dogs. Walking in the fresh air and exercising will help you maintain overall fitness and strengthen your immune system.
If you suspect the development of a sebaceous gland adenoma, it is recommended to regularly examine the dog and contact a veterinarian at the first signs of the disease.
In general, a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, regular dog hygiene, and timely consultation with a veterinarian will help prevent the occurrence of sebaceous gland adenoma and maintain the health of your pet.
When To Consult A Veterinarian?
Consult your veterinarian if you discover a cyst on your dog’s skin. A benign cyst cannot be mistaken for a malignant tumor by an amateur. If you observe any of the following symptoms in addition to a cyst you need to speak with a veterinarian:
- The cyst is bloody or painful;
- The volume of the cyst increases over time;
- Your dog has a fever;
- The cyst is purulent;
- Other cysts appear.
In some cases, even a benign sebaceous cyst can become affected by germs and lead to an infection that can endanger the dog’s health. The seriousness of a cyst should never be underestimated.
Treatment Of Sebaceous Gland Adenoma in a Dog:
Treatment of sebaceous gland adenoma in a dog depends on the degree of development of the tumor, its location, age, and general condition of the pet. In most cases, when the tumor is small and does not cause discomfort, the veterinarian recommends observation and regular examination of the animal.
If the size of the sebaceous adenoma increases significantly or your pet experiences discomfort or pain, surgery may be recommended. The surgery involves removing the tumor and surrounding healthy tissue.
Despite the fact that surgical removal of sebaceous gland adenoma provides good predictability and a high success rate, it should be noted that relapses are possible. Therefore, after surgery, regular monitoring and monitoring of the dog’s health will be necessary.
Depending on the stage and evolution of the lump, various therapies may be used if a veterinary examination confirms the presence of a sebaceous cyst.
Unpierced Sebaceous Cyst:
If the cyst is not burst, there are different solutions to treat it. You should know that in the majority of cases, applying an anti-infectious ointment for 4 to 6 days is enough to make a sebaceous cyst disappear. When faced with a benign cyst, your veterinarian may simply suggest that you wait until it resolves on its own.
If the dog’s sebaceous cyst becomes infected, antibiotic treatment must be prescribed to fight the infection. In the most serious cases, surgical intervention (very rare) under general anesthesia may be necessary.
Pierced Sebaceous Cyst:
Warning: if the sebaceous cyst bursts on its own, it is imperative to empty it completely and treat it to avoid bacterial infection.
It’s common for dogs to lick a ruptured cyst, which can lead to a significant infection. To completely empty the cyst, use a dog disinfectant and prevent your dog from licking its wounds. The use of a healing cream may also be advisable. If in doubt, it is best to consult your veterinarian.
Conclusion:
However, if the adenoma turns out to be malignant or has already metastasized to other organs, the prognosis may be less favorable. In such cases, additional treatments such as surgical removal of the tumor, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy may be needed to improve the chances of recovery.
It is important to note that regular visits to the veterinarian, screening examinations, and early detection of sebaceous adenoma in a dog can significantly improve the prognosis of the disease. Regular self-examination and examination of the dog’s skin can also help identify changes in the sebaceous glands and obtain timely consultation with a specialist.